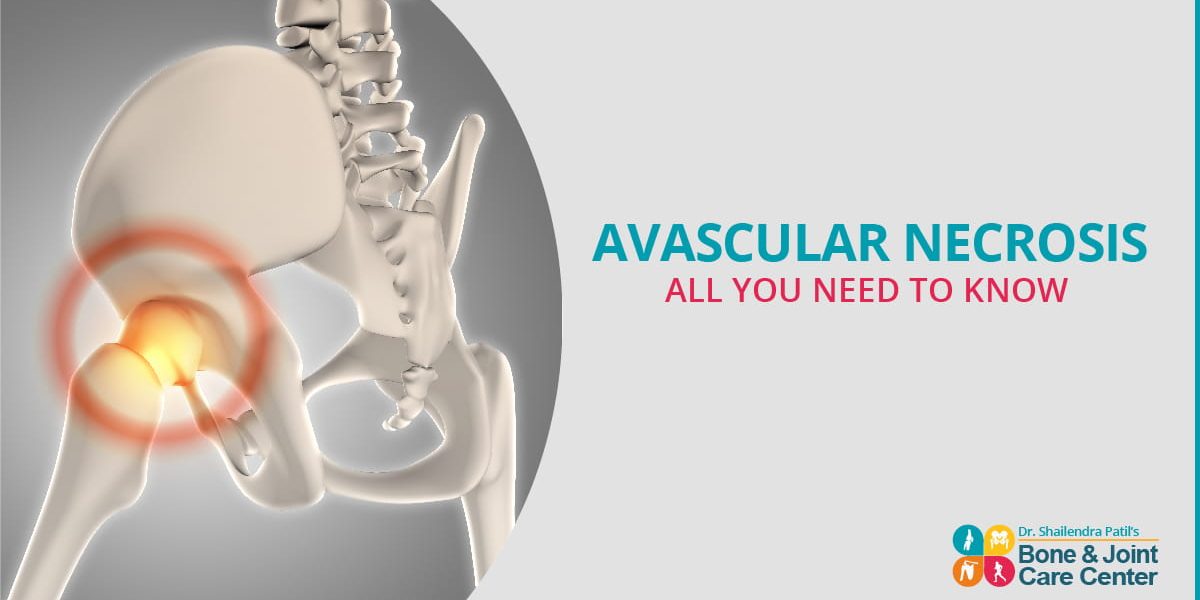
Avascular Necrosis, commonly known as Osteonecrosis, is a medical condition in which the tissue within the bone dies because of the deficiency of blood supply. Before the tissues collapse, Osteonecrosis causes small breaks within the human bone structure (which eventually breakdowns the tissues within the bone). Proper blood supply is required by all cells in your body and when the tissues within your bone do not get sufficient amount of blood, they die. While hip is considered one of the most vulnerable areas to this medical condition, Avascular Necrosis may also affect your knee, shoulder, foot, and hand.
Avascular Necrosis may show no symptoms at all in the initial stage. But later on, when the blood supply to the tissues within your bone breaks off, the patient may start noticing from little to severe pain in the affected joint. The pain worsens when you lift up heavy objects or put a significant amount of weight to the particular joint. The first symptom of Osteonecrosis is the pain, which can be mild or severe depending on the stage of the condition and the weight you put on that joint. You may also feel this pain while lying down or performing no activity at all. The pain starts from the middle of the groin area and spread out to the buttock and thigh. In 4-5 out of 10 cases, the patients may develop bilateral Avascular Necrosis (a condition in which the bones of both hip joints collapse). Consult with your doctor if you observe a mild or severe pain near the groin, buttock, and thigh that gets intense with time.
Causes of Avascular Necrosis
Avascular Necrosis can happen to people of any age. However, adults of age 25-50 are at higher risk. As mentioned above, the main cause of Avascular Necrosis is the stoppage of the blood supply within the bone. This mainly occurs because of the following reasons:
- Joint or Bone Injury: A serious trauma or an injury can destroy the adjacent blood vessels, cutting the blood supply to your bones.
- Fatty Deposits: The fatty deposits can be another leading cause of Avascular Necrosis. The lipids are capable of blocking your blood vessels which eventually blocks the blood supply to your tissues. Fatty deposits are likely to form in the small-sized blood vessels of human who consume an excessive amount of alcohol.
- Certain Medical Conditions: The patients suffering from sickle cell anemia or Gaucher’s disease are at higher risks of Avascular Necrosis than normal people. The chemotherapy and kidney transplantation can also weaken your blood vessel, obstructing the blood supply within your bone. It is important to note that certain ailments, such as Diabetes, HIV, Pancreatitis, and more, increase the risk of Avascular Necrosis.
- Unknown causes: One-fourth of the Osteonecrosis cases occur due to unknown causes.
Stages of Avascular Necrosis
There are multiple ways of diagnosing Avascular Necrosis condition and its stage. AVN staging system is one of the most common yet effective ways of examining your joints and discovering the issue. The other effective tests include radiology, MRI, and CT scan. There can be a total of 13 stages, starting from stage 0 to stage 4th in Avascular Necrosis.
Stage 0 :The patient is believed to be in stage 0 of Avascular Necrosis when he witnesses no symptoms of the ailment and the tissues look normal in the radiology findings yet histology indicates Osteonecrosis.
Stage 1 :Stage 1 suggests the possibility that the patient might not be witnessing symptoms. The radiology findings suggest ‘unremarkable’ results, an MRI suggests the possibility of AVN, and the blood reports are not normal.
Stage 2 : In Stage 2, the patient is likely to observe and display the symptoms of Avascular Necrosis. The radiology findings are abnormal whereas the MRI detects Avascular Necrosis.
Stage 3 :Radiology findings detect Subchondral Lucency.
Stage 4 :Stage 4 suggests the flattening or breakdown of the femur’s head as well as susceptible CT scan and abnormal joint space. Stage 4 is further divided into three stages i.e. stage 4a (15% of noticeable collapse), stage 4b (15-30 percent of collapse), and 4c (30% of the visible collapse of the head of the femur).
Stage 5 :Contraction of joints is seen on radiography scan.
Stage 6 : The final stage of Avascular Necrosis indicates significant damage to the head of the femur and the affected joint.
Treatment for Avascular Necrosis
The main objective of the Avascular Necrosis treatment is to alleviate the painful symptoms and keep the bones and tissues within it from further loss. Sometimes, the specialists may be able to cure the disease conservatively. But some cases may require the combination of surgical and conservative treatment.
- The doctors may recommend pain killers and osteoporosis medication.
- Hip exercises coupled with physiotherapy
- Changes in the lifestyle such as limitation or prevention of alcohol to keep the lipid from obstructing blood vessels.
Surgical Treatment: Most of the times, Avascular Necrosis is diagnosed in its later stages i.e., when the condition has progressed to an extent where medication or lifestyle changes may not work. In such cases, orthopedic suggests surgery as the ultimate resort. There are mainly three surgical treatments for Avascular Necrosis:
- Core Decompression
- Total hip replacement
- Bone reshaping
Regenerative Medical Treatment: This treatment is the most sophisticated procedure for Avascular Necrosis patients in the early stages. The specialists take out the stem cells of the bone marrow of the patient and put it in place of the collapsed bone.
Final Words
Avascular Necrosis shows little to no symptoms in its early stage. That’s why it is mostly diagnosed in the later stages (when the condition has progressed and surgery seems the only reliable treatment). If left untreated, Avascular Necrosis can damage your bone completely leading to a serious medical condition i.e. Severe Arthritis.